OER_at_Co3O4(111)
Type: Catalysis Results (png) show more
ObjectId: 38282
Created: 12/15/2025 4:57:00 PM by A06) Dhaka Kapil [kapil.dhaka@uni-due.de]
Updated: 12/15/2025 4:57:19 PM by A06) Dhaka Kapil [kapil.dhaka@uni-due.de]
Access: Public Sort Code (asc): 10
License: CC BY 4.0
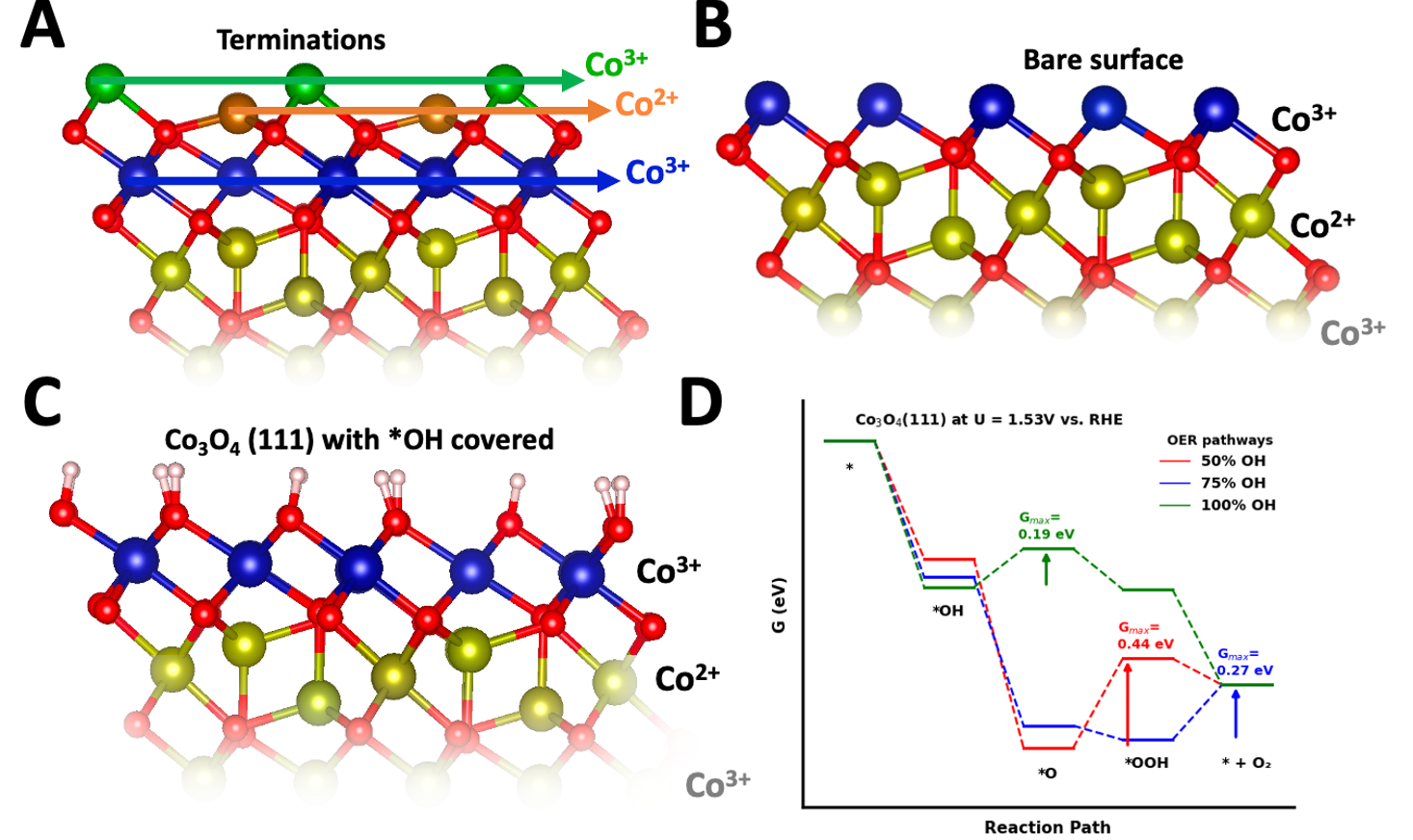
Description: Structural models and reaction energetics of OER on Co 3 O4 (111) with different hydroxyl (*OH) coverages. a) Different possible terminations of theCo 3 O4 {111} facet, highlighting the selected Co-rich Co 3+ termination. b) Bare Co-rich Co 3+ terminated Co 3 O4 (111) surface. c) Hydroxylated Co 3 O4 (111)termination, showing the adsorption configuration of *OH groups. d) Free energy diagram for OER at U = 1.53 V versus RHE, comparing 8OH, 12OH, and16OH coverages. The equation was done using descriptor-based analysis (descriptor Gmax (U)), assuming the mononuclear OER mechanism.[69] The limitingsteps are indicated by arrows in blue, green, and red with the corresponding activation energy.
File attached: OER_at_Co3O4(111).png 668.2 Kb
Referenced Objects (Reverse Association)
-
ChemCatChem 2025 (Schellenburg)
PublicationD. Schellenburg, T. Bihnam, C. Placke-Yan, G. Bendt, O. Prymak, T. Sato, D. Jennings, C. Leiva-Leroy, D. Zhang, M. Nachev, K. Dhaka, F. Nkou, U. Hagemann, M. Heidelmann, S. Kenmoe, K. S. Exner, B. Sures, M. Muhler, C. H. Liebscher, A. Schnegg, S. Schulz, S. Barcikowski, S. Reichenberger, “Mechanistic Understanding of Laser-Induced Defect Engineering of Anisotropic Cobalt Oxide Spinel Platelets in Water,” ChemCatChem, 2025, 17, e202501054. DOI: 10.1002/cctc.202501054.
ChemCatChem - 2025 - Schellenburg - Mechanistic Understanding of Laser‐Induced Defect Engineering of Anisotropic Cobalt.pdf
All properties (except table)
No properties found